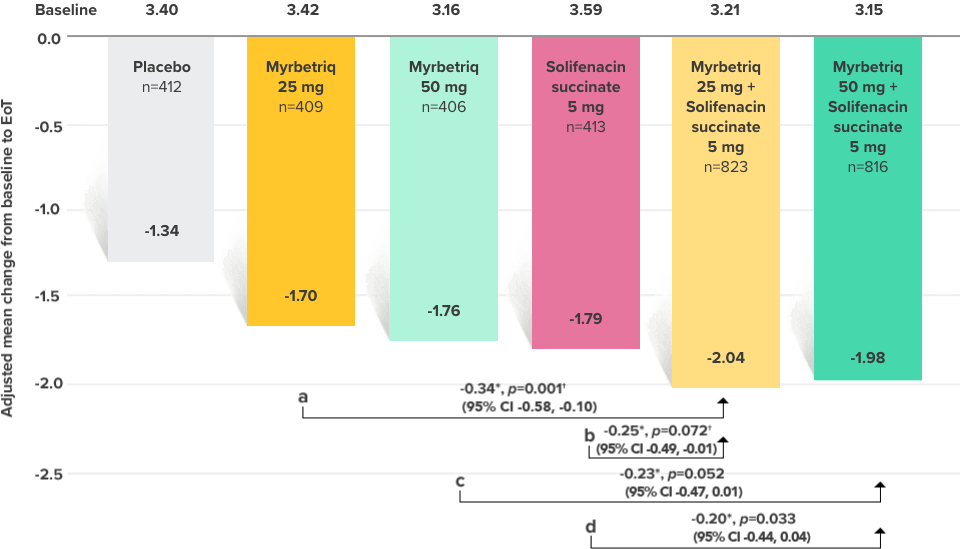
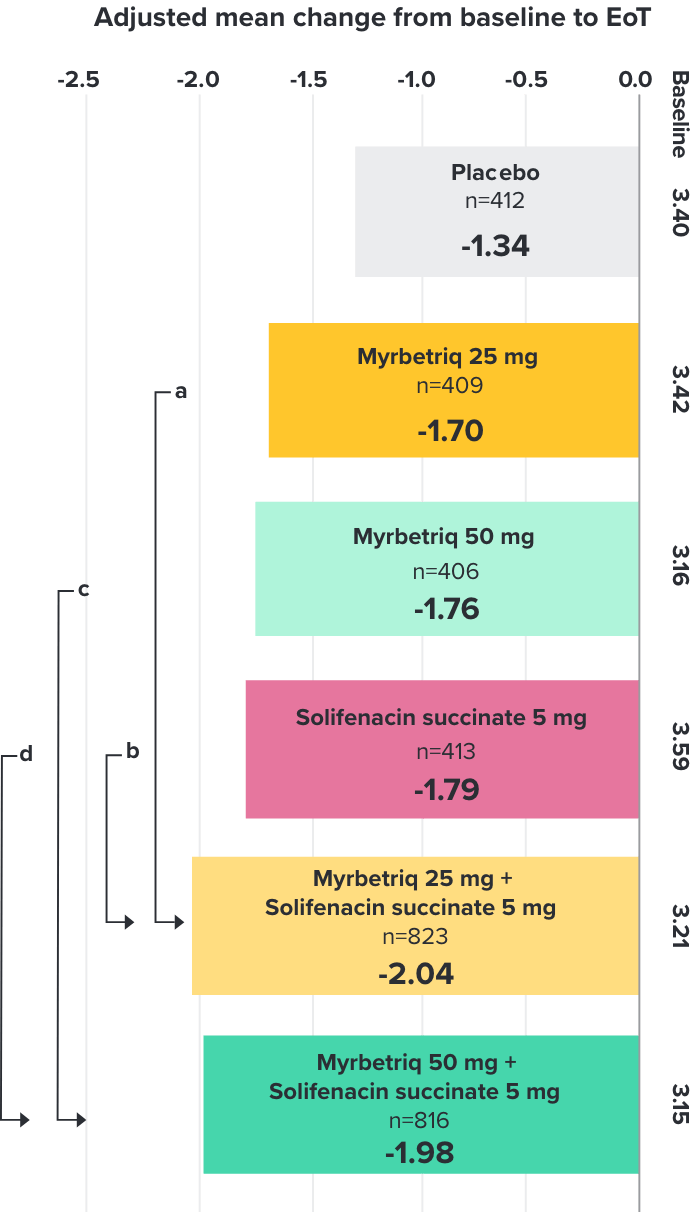
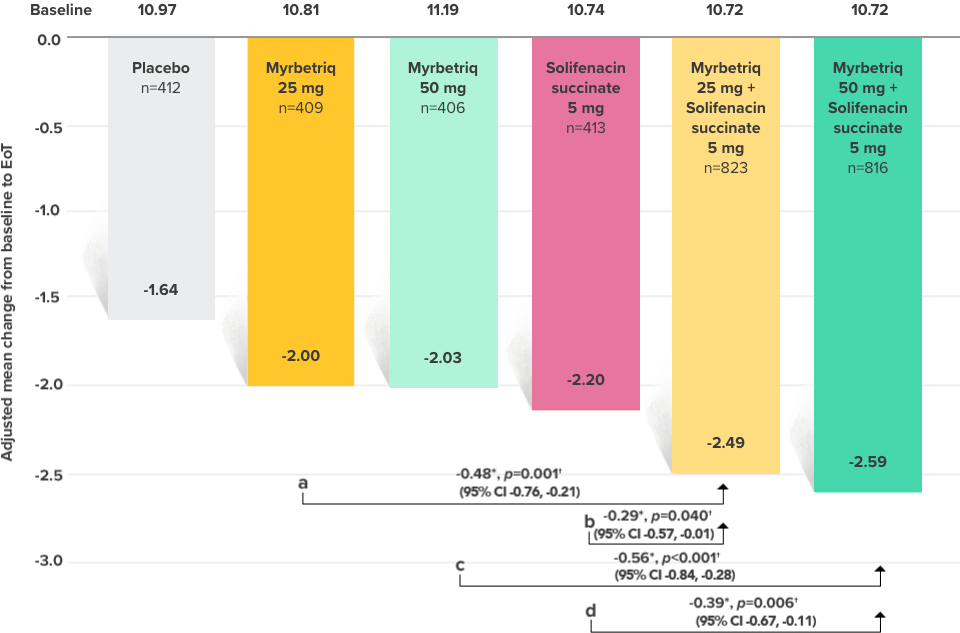
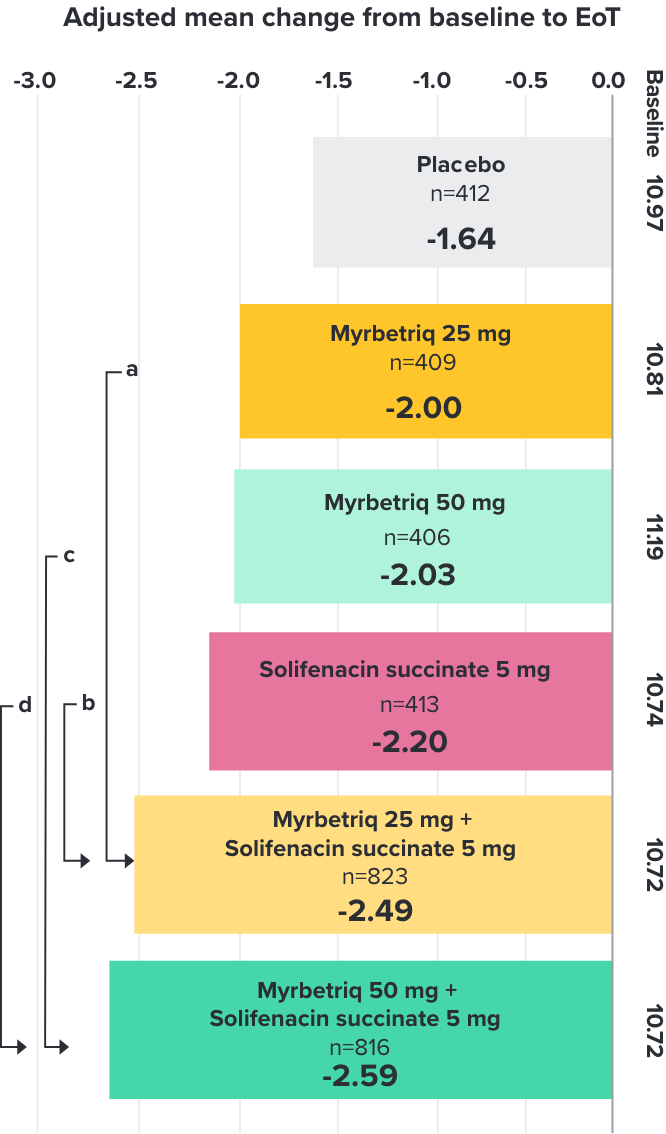
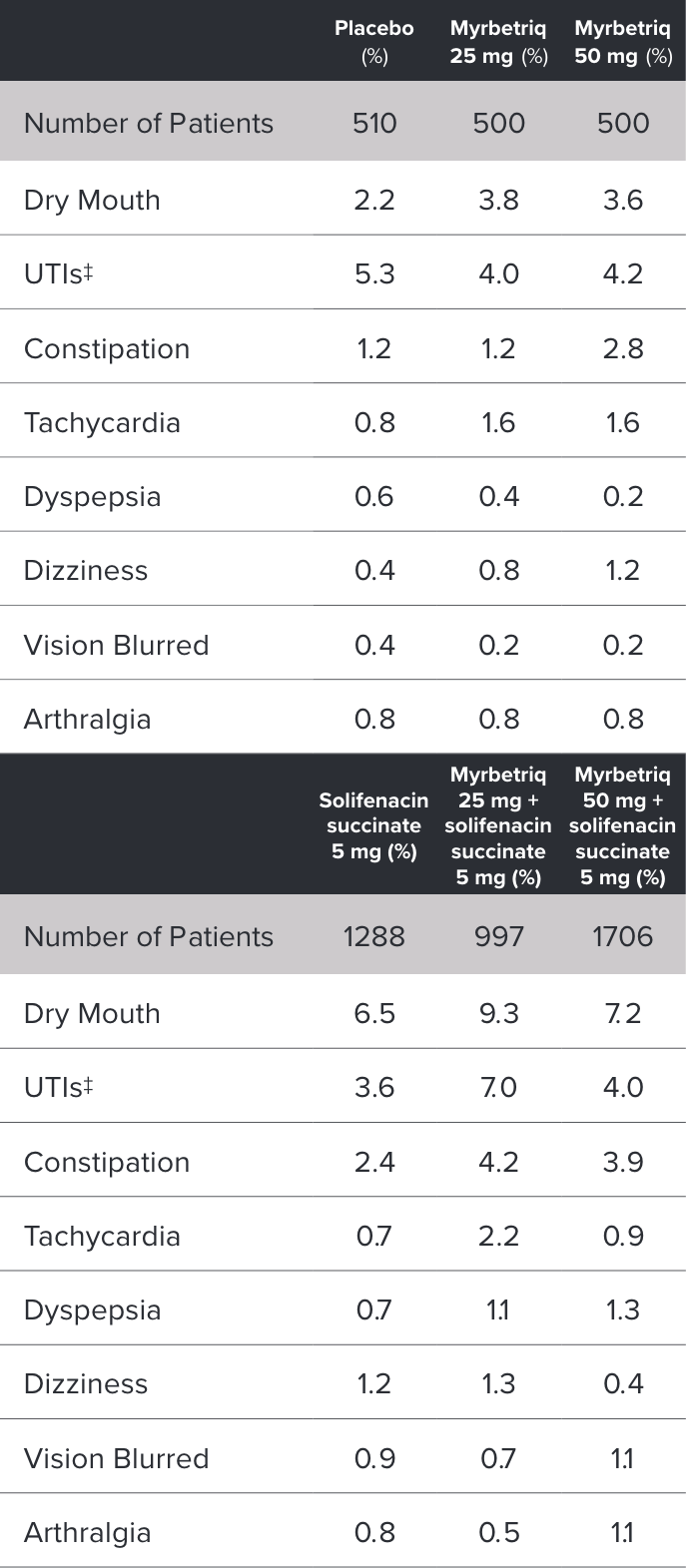
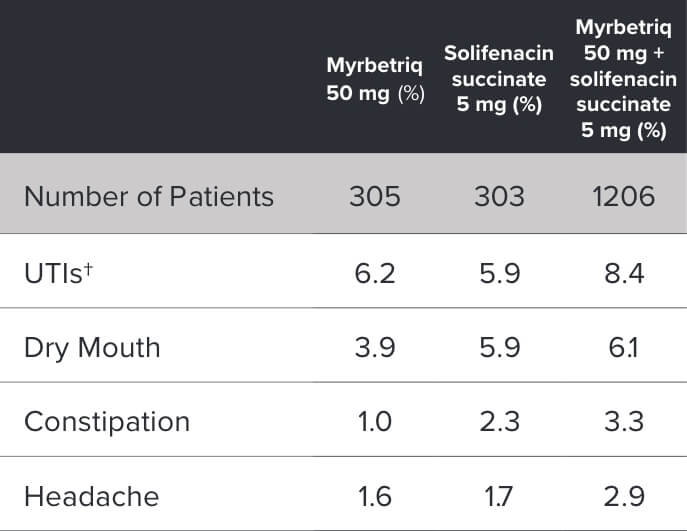
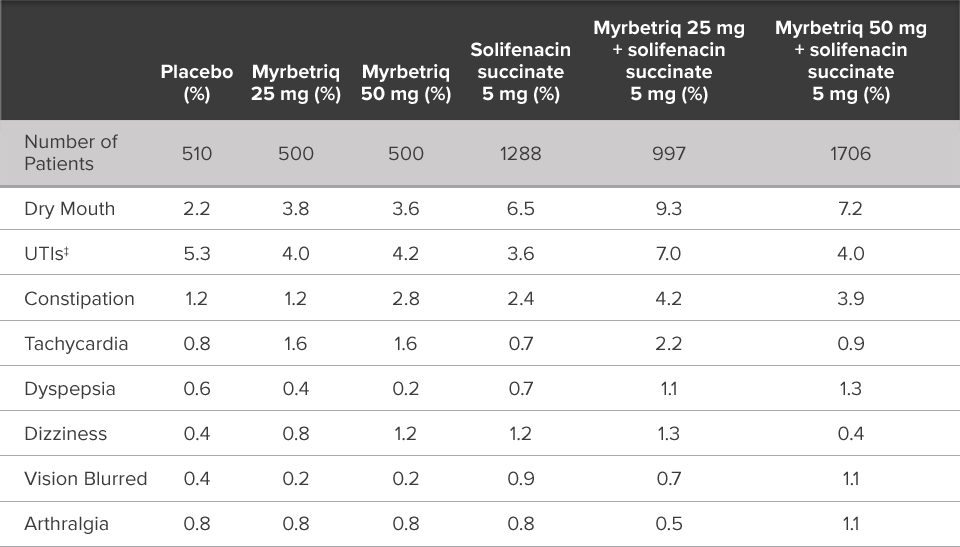
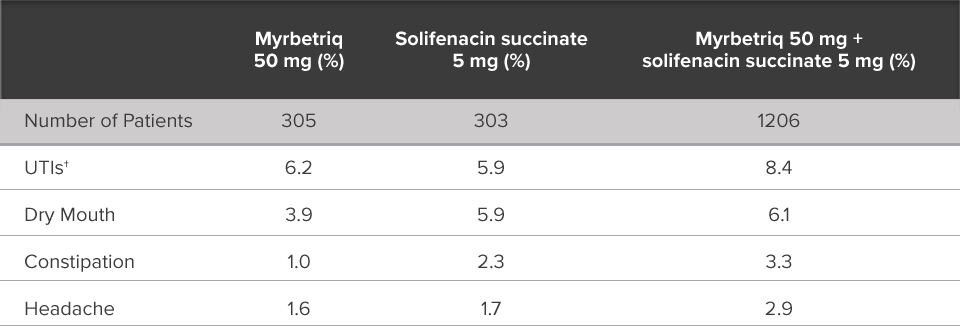
Demonstrated reduction in incontinence
Myrbetriq added on to solifenacin succinate showed meaningful reduction in incontinence episodes per 24 hours1,10
Primary Endpoint
Adjusted change from baseline to end of treatment (Week 12) in mean number of incontinence
episodes per 24 hours1
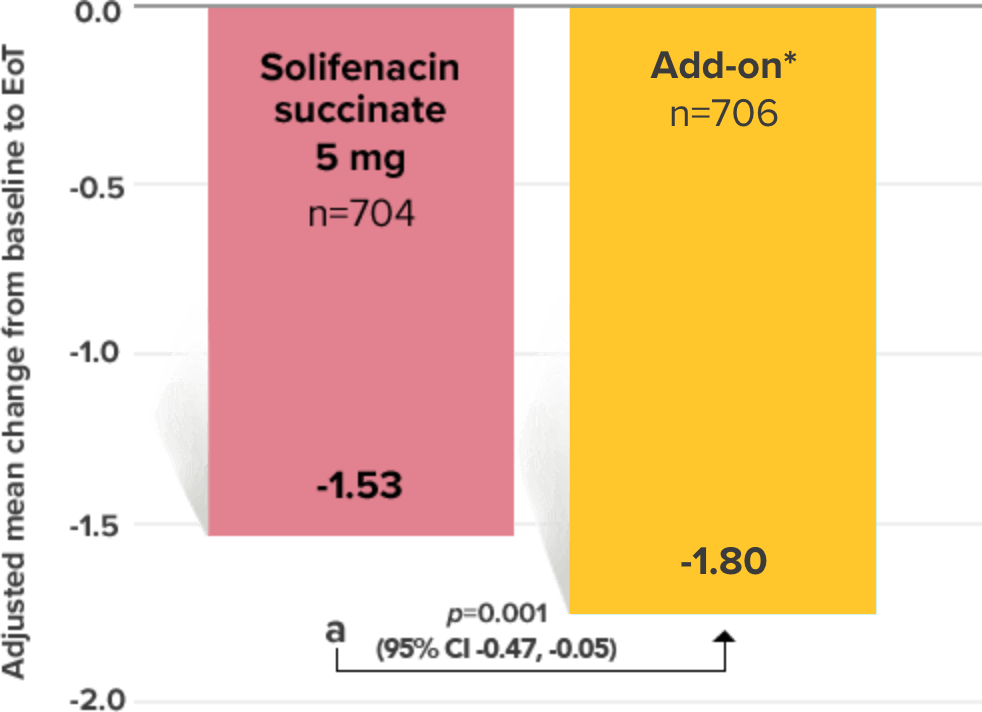
a Add-on therapy demonstrated significant improvement vs solifenacin succinate 5 mg (p=0.001).
CI = confidence interval; EoT = end of treatment.
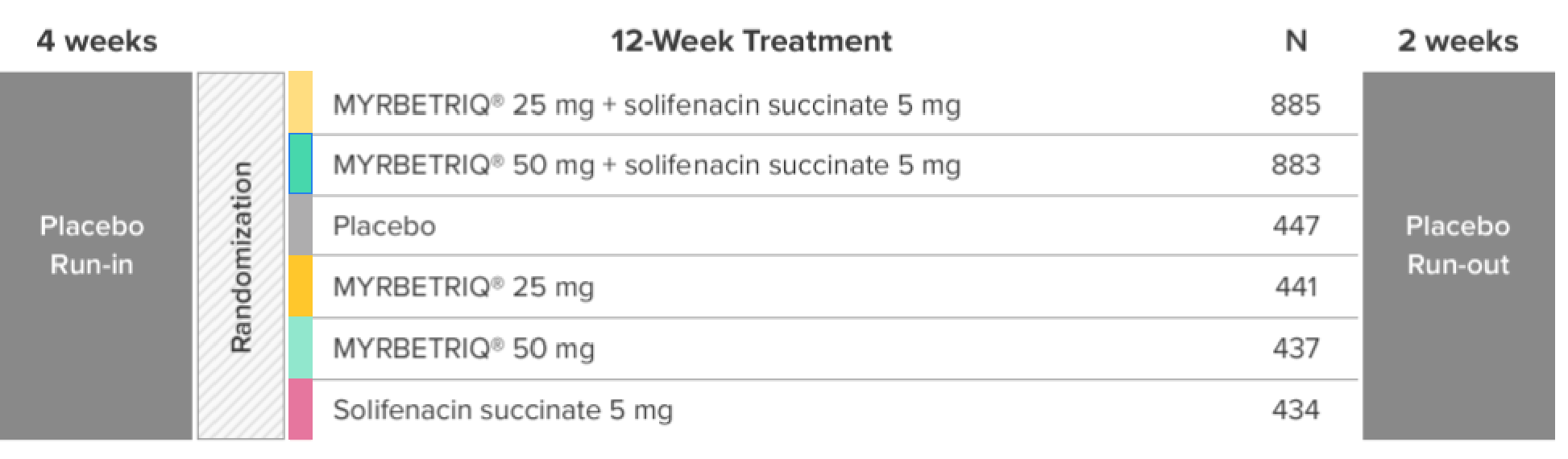
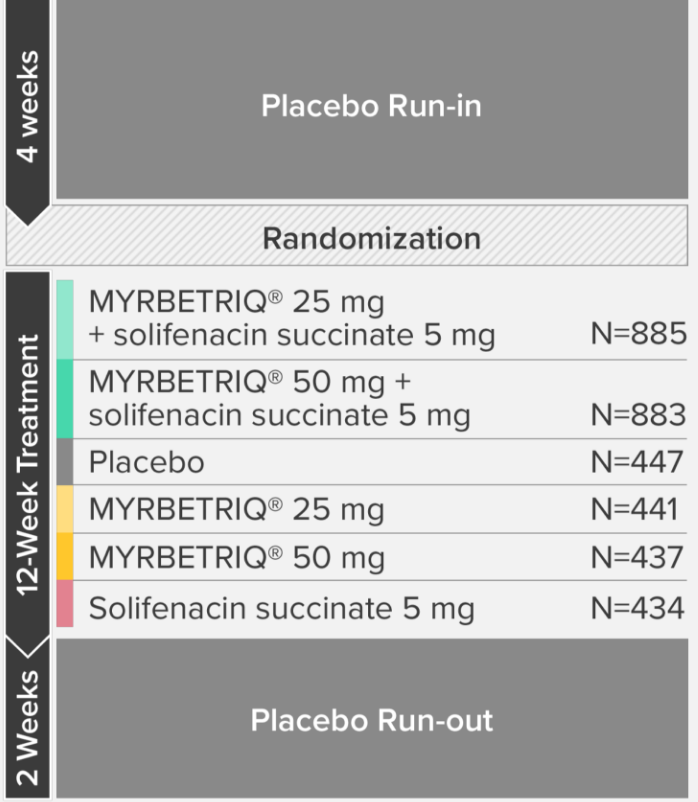
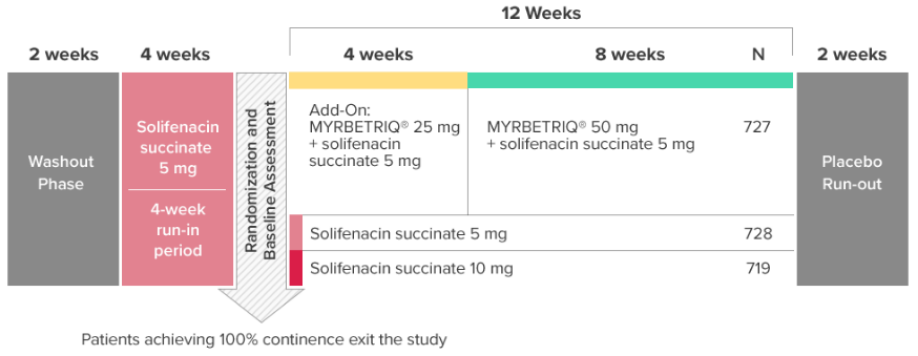
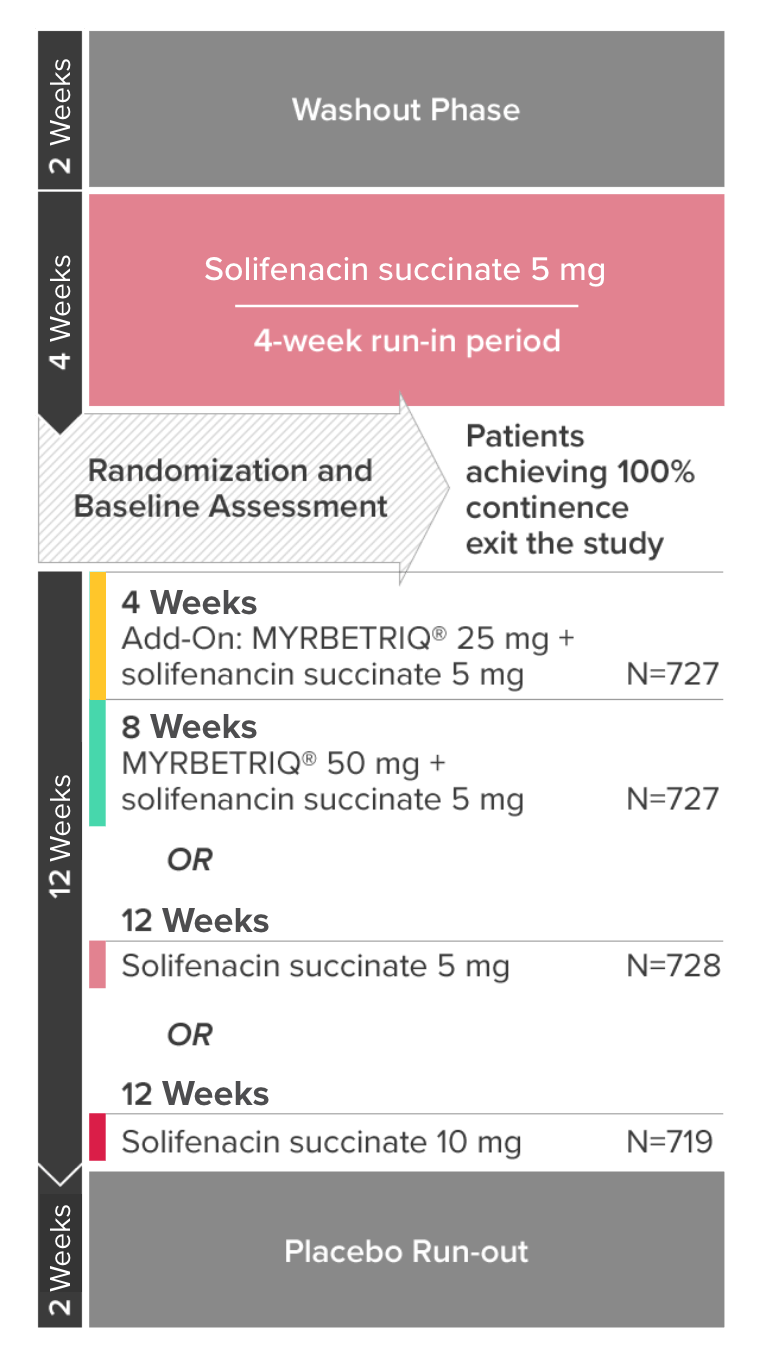
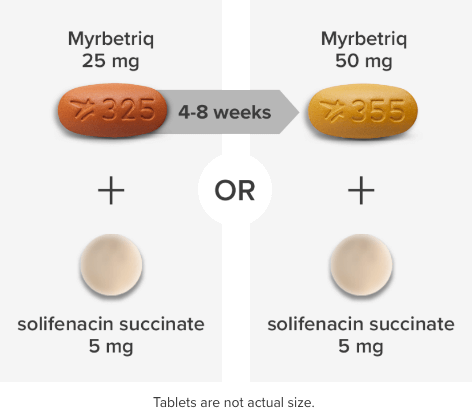
*Patients in the add-on therapy treatment group received Myrbetriq 25 mg and solifenacin succinate 5 mg for 4 weeks. The Myrbetriq dose was increased to 50 mg after Week 4.1
- 46% of patients receiving Myrbetriq add‑on therapy achieved zero incontinence vs 37.9% of patients receiving solifenacin succinate 5 mg alone (odds ratio 1.47 (95% CI 1.17, 1.84))10
Demonstrated reduction in micturition frequency
Myrbetriq added on to solifenacin succinate showed meaningful reduction in micturition frequency per 24 hours1
Secondary Endpoint
Adjusted change from baseline to end of treatment (Week 12) in mean number of micturitions per 24 hours1,10
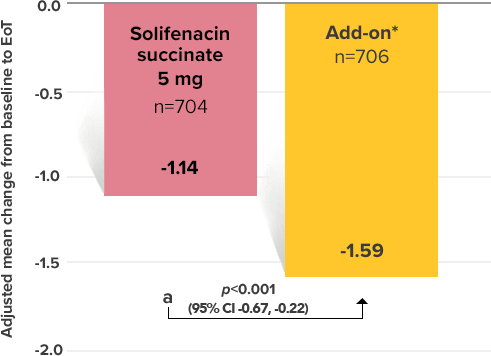
a Add-on therapy demonstrated significant improvement vs solifenacin succinate 5 mg (p<0.001).
CI = confidence interval; EoT = end of treatment.
*Patients in the add-on therapy treatment group received Myrbetriq 25 mg and solifenacin succinate 5 mg for 4 weeks. The Myrbetriq dose was increased to 50 mg after Week 4.1
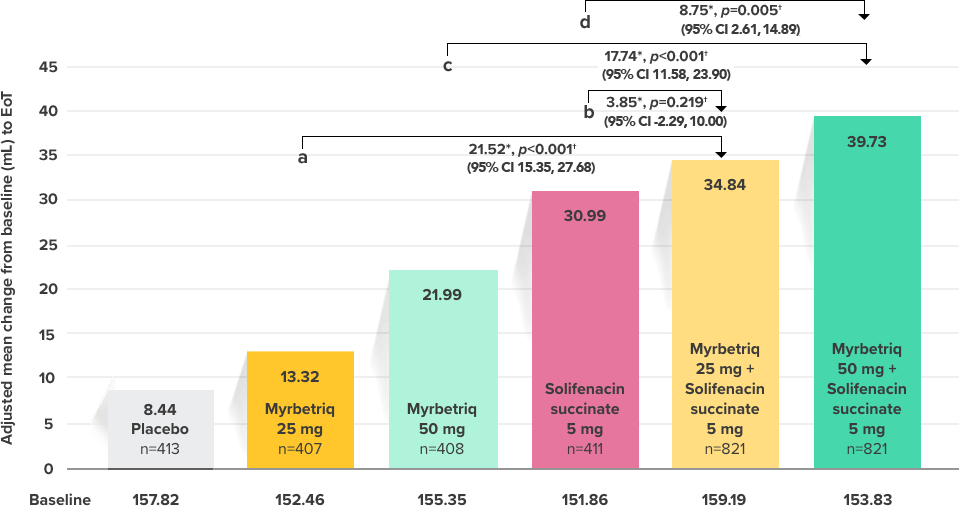
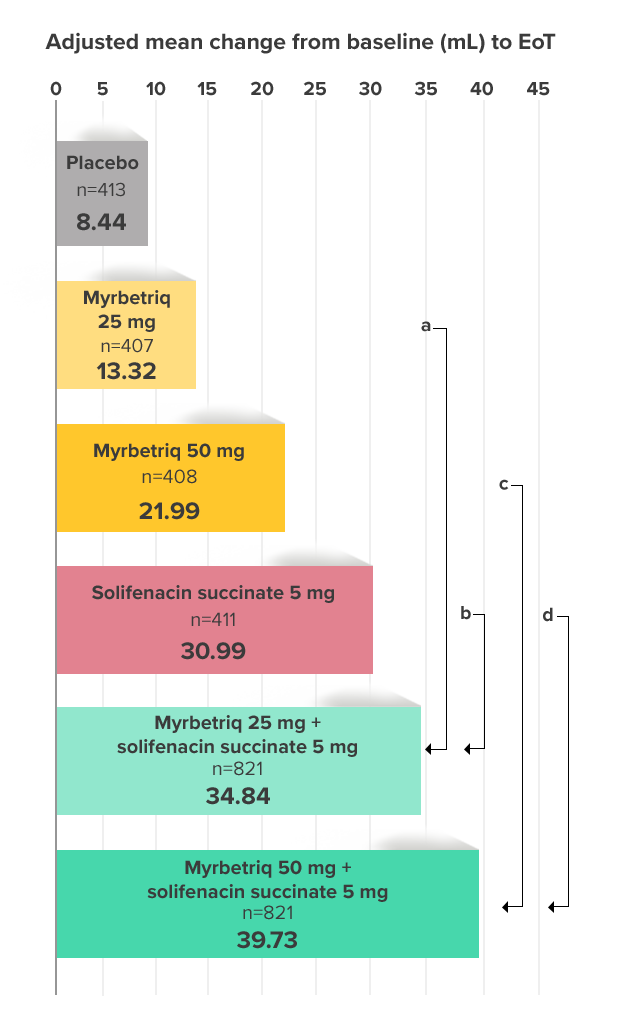
Demonstrated increase in volume voided per micturition
Myrbetriq added on to solifenacin succinate increased the mean volume voided per micturition1
Secondary Endpoint
Adjusted change from baseline to end of treatment (Week 12) in mean volume voided per micturition1,10
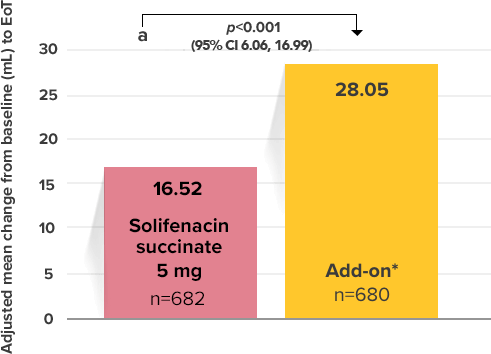
a Add-on therapy demonstrated significant improvement vs solifenacin succinate 5 mg (p<0.001).
CI = confidence interval; EoT = end of treatment.
*Patients in the add-on therapy treatment group received Myrbetriq 25 mg and solifenacin succinate 5 mg for 4 weeks. The Myrbetriq dose was increased to 50 mg after Week 4.1